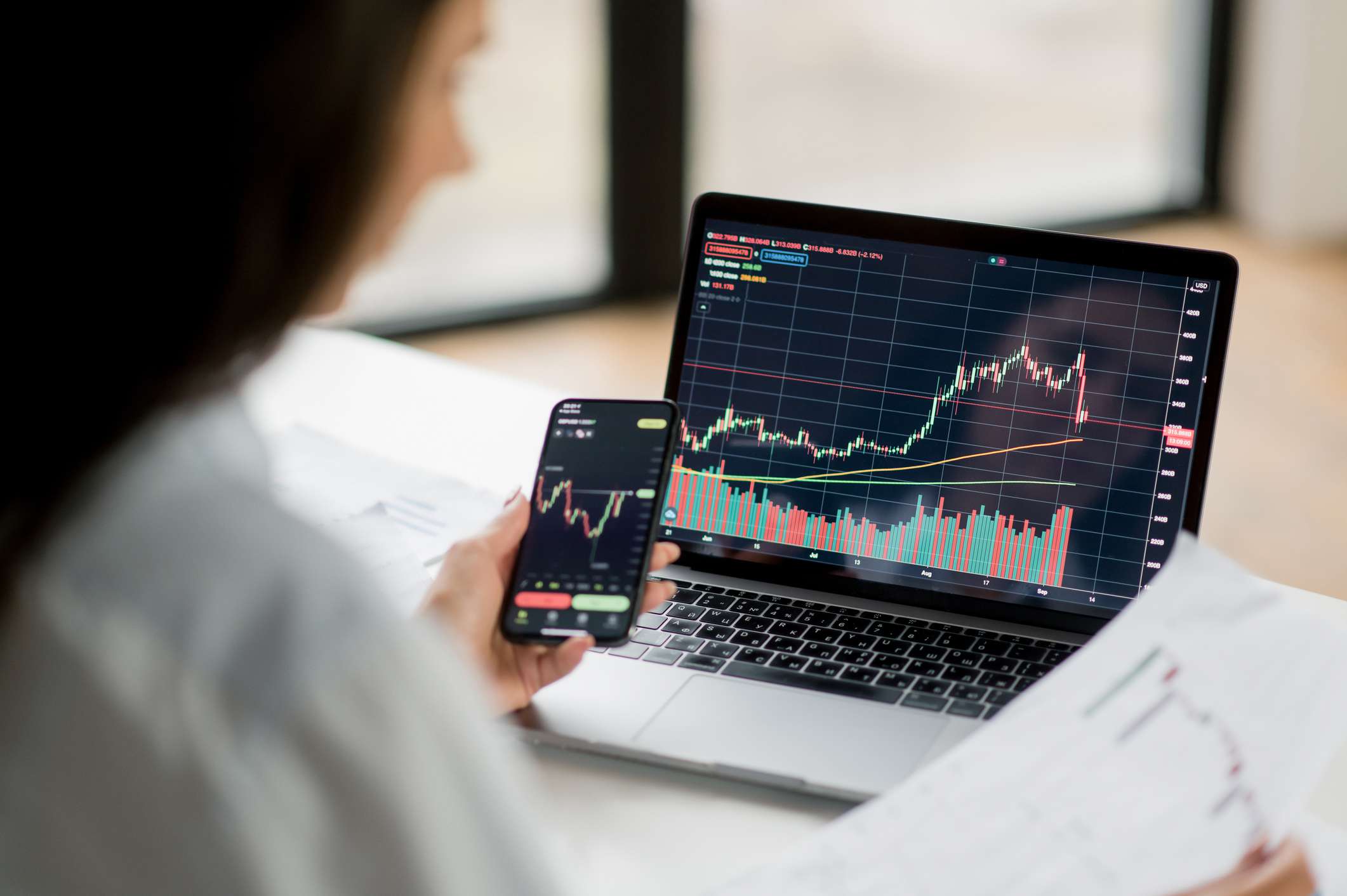
Are you interested in exploring effective intraday trading strategies? One approach worth considering is gap trading. In this article, we will delve into the world of gap trading, discussing what it entails, the different types of gaps, and strategies to capitalize on them. Whether you are a seasoned trader or just starting, understanding gap trading can be a valuable addition to your trading toolkit.
Introduction
Intraday trading, also known as day trading, involves the buying and selling of financial instruments within the same trading day. It requires traders to make quick decisions based on short-term price fluctuations. Gap trading, a popular intraday trading strategy, focuses on exploiting price gaps that occur on a chart.
What is Intraday Trading?
Before diving into gap trading, let’s briefly recap what intraday trading is. Intraday traders aim to profit from the price movements that occur within a single trading day. Unlike long-term investors who hold positions for weeks or months, intraday traders enter and exit trades within the same day, avoiding overnight exposure to market risks.
Understanding Gap Trading
In the financial markets, a gap refers to a significant price difference between the closing price of a security and the opening price of the next trading session. Gaps occur when there is a sudden shift in supply and demand dynamics, leading to a discontinuity in the price chart. Gap trading strategies capitalize on these gaps and aim to profit from the subsequent price movement.
Types of Gaps
There are four main types of gaps that can occur in price charts: common gaps, breakaway gaps, continuation gaps, and exhaustion gaps.
- Common Gaps: These gaps occur in regular market conditions and are typically small in size. They do not signify a major shift in market sentiment and are often filled quickly.
- Breakaway Gaps: Breakaway gaps emerge at the beginning of significant price trends. They indicate a change in market sentiment and can be an early indication of a new price direction.
- Continuation Gaps: Continuation gaps occur within an existing price trend and represent a temporary pause or consolidation before the trend resumes. Traders often look for continuation gaps as potential entry points to join the ongoing trend.
- Exhaustion Gaps: Exhaustion gaps form near the end of a price trend and indicate the last surge of buying or selling pressure before a reversal. These gaps can signal an imminent trend reversal.
Strategies
To effectively trade gaps, traders employ various strategies based on the type of gap and their trading objectives. Let’s explore four common gap trading strategies:
Strategy 1: Gap Fill
The gap fill strategy aims to profit from the price returning to fill the gap. For common gaps, where the price tends to revert quickly, traders anticipate the price to move back to the pre-gap level, providing a trading opportunity.
Strategy 2: Breakaway Gap
Breakaway gaps often accompany strong price moves and indicate a shift in market sentiment. Traders utilizing the breakaway gap strategy aim to capture the momentum of the new trend and enter positions in the direction of the gap.
Strategy 3: Continuation Gap
Continuation gaps occur within an ongoing trend and present an opportunity to join the trend at a favorable price. Traders using the continuation gap strategy look for gaps that signal the resumption of the existing trend and enter positions accordingly.
Strategy 4: Exhaustion Gap
Exhaustion gaps indicate the end of a price trend and a potential reversal. Traders employing the exhaustion gap strategy anticipate a reversal and enter positions opposite to the direction of the gap, aiming to profit from the subsequent price correction.
Important Considerations
While gap trading can be profitable, it is essential to consider a few key factors:
- Volume Analysis: Analyzing volume patterns can provide insights into the strength and validity of a gap. Higher volume during gap formations can signify increased market participation and validate the trading opportunity.
- Market Context: Understanding the broader market context, including overall trends and market sentiment, can help gauge the reliability of gap trading opportunities. It is crucial to align gap trades with the prevailing market conditions.
- Risk Management: Implementing proper risk management strategies is vital in any trading approach. Setting stop-loss orders, defining risk-reward ratios, and practicing disciplined trade management can help mitigate potential losses.
Risk Management
Managing risk is crucial when implementing any trading strategy, including gap trading. Here are a few risk management techniques to consider:
- Stop-loss Orders: Placing stop-loss orders helps limit potential losses if the trade goes against you. Determine an appropriate stop-loss level based on your risk tolerance and the characteristics of the gap being traded.
- Position Sizing: Proper position sizing ensures that each trade’s potential loss is within your acceptable risk limits. Avoid overexposure to any single trade by allocating a percentage of your trading capital to each position.
- Diversification: Spreading your trading capital across multiple gaps and different market sectors can help reduce the impact of individual trade outcomes and provide a more balanced risk profile.
Technical Indicators for Gap Trading
Technical indicators can complement gap trading strategies and provide additional confirmation signals. Here are a few commonly used indicators for gap trading:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages help smooth out price fluctuations and identify the underlying trend. Traders often use moving averages in combination with gap trading strategies to confirm the trend direction.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum oscillator that measures the speed and change of price movements. It can help identify overbought or oversold conditions, potentially aiding in gap trading decisions.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands consist of a moving average, an upper band, and a lower band. These bands help identify periods of price consolidation and potential breakouts, which can be valuable for gap traders.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
As with any trading approach, there are common pitfalls that gap traders should be aware of and avoid:
- Chasing Gaps: FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) can lead traders to chase gaps without proper analysis or consideration of risk. It is important to exercise patience and wait for favorable trading setups.
- Ignoring Market Context: Trading gaps solely based on their presence without considering the broader market context can be risky. Ensure that gap trading opportunities align with the prevailing market conditions and trends.
- Lack of Risk Management: Neglecting risk management principles can lead to significant losses. Always define your risk tolerance, set appropriate stop-loss levels, and adhere to disciplined trade management.
Conclusion
It is a popular intraday trading strategy that involves capitalizing on price gaps that occur on charts. By understanding the different types of gaps and employing suitable strategies, traders can potentially profit from these market discontinuities. However, it is crucial to consider important factors such as risk management, market context, and technical indicators to enhance the effectiveness of gap trading. Remember to practice discipline, patience, and continuous learning to improve your gap trading skills.